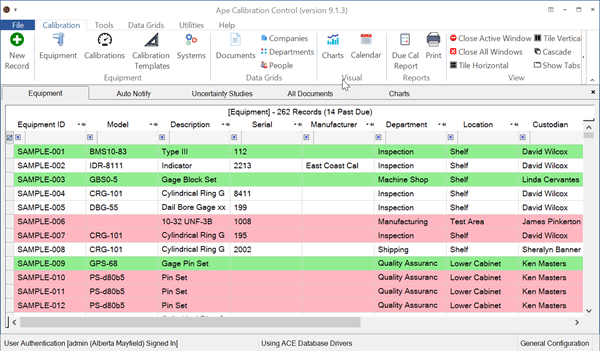
Security Methods
Audit Trails & Roles Permissions
Calibration Control (our Calibration Management Software) has measures and options to help you maintain the security and integrity of your data. In aditional to global settings of security methods and logging for audit trails, the Hierarchy of User Roles can help you enforce security restrictions or grant permissions to various users accessing your database.
Compliance
For more information about 21-CFR-Part-11 compliance within software features to help you meet federal regulations, refer to the FDA Compliance article.
Database Security
When using a MS SQL Server database in Calibration Control, the built-in SQL Server and Windows authentication methods will keep the database protected. Otherwise, when using MS Access the database file (apecal.mdb) can use an encrypted database password.
The Change Log
Audit all field and label changes which are tracked in the Change Log grid found in the Data Grids tab of the ribbon menu. It records time and date, user name (if signed in), the screen where the changes were made, machine (computer) name, and the detail of the change. The change detail includes field names and before/after data.
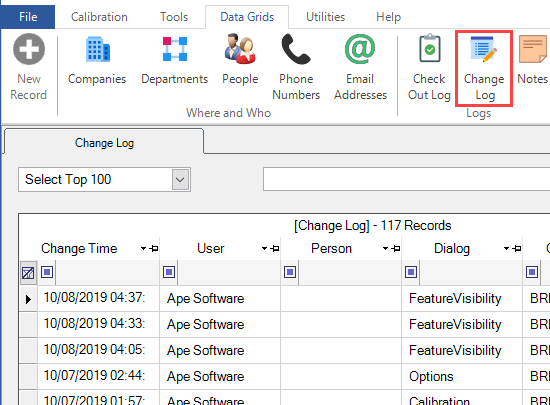
The Check Out Log
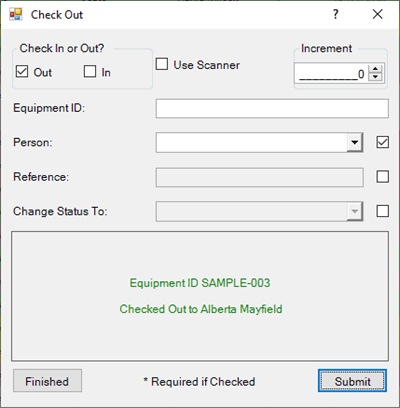
All history of job records and tool activity with the Check Out activity dialog is recorded in the Check Out log found in the Data Grids tab of the ribbon menu. It records the time and date of both check in and check out actions, the increment, the Equipment ID. The Check Out log also records Machine name, Created date, and Created By User name. If applicable, log shows the name of the Person for the Check Out, the Reference information, and Status Changed To value, if applicable. Set the requirements for Check Out in program Options.
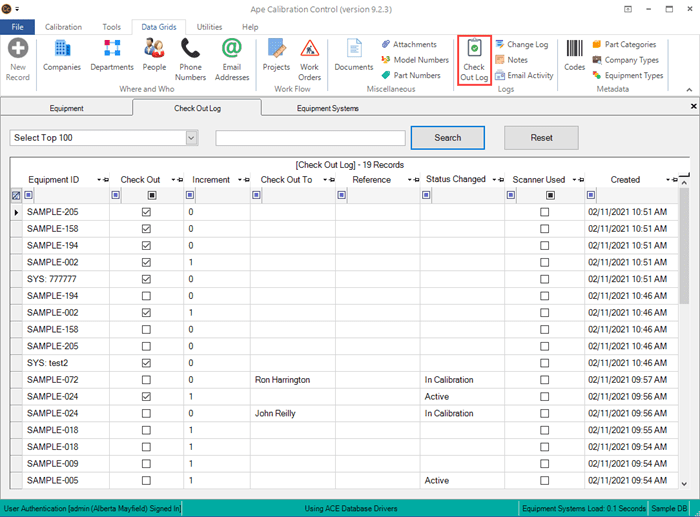
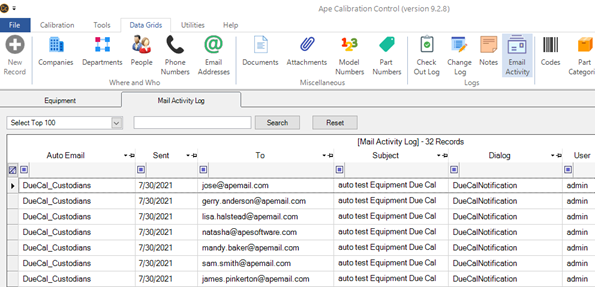
The Mail Activity Log
All history of Auto-Notifications scheduled to send automatically or manually triggered Emails are logged in detail in the Mail Activity log, found in the Data Grids tab of the ribbon menu. View the history log for emails sent from the database, when, and from whom. The Mail Activity Log records the Auto Email Event and Dialog name, Sent date, Recipient Emails, CC and BCC Email Addresses, Content Subject Bar, Signature File Name, Email Body, User name, and Person name.
User Roles Privileges & Permissions
Authentication methods including helping you restrict user access and permissions by designating roles and then editing specific roles required for various permissions.
Activate User Authentication (Sign-In Mode)
Administrator Role Privileges
Administrators have full access to all parts of the application that require any level of security. An Admin can create Users and change the Role privileges of Users, including other Admins. Administrators cannot remove themselves from being an Admin while User-Authentication mode is activated; one Admin must remove the Admin privileges of another. This is a safety feature to ensure there is at least one Admin while the application is in User Authentication mode.
Users' Passwords
When an Administrator creates or changes the password for any User other than themselves, that User can be given a temporary password to change once they sign in for the first time. Use the Password Security Dialog page for help in implementing and adjusting Password Security methods.
Pre-Defined Permissions
There are pre-defined permissions for specific areas of the application that require a given level of security. Although each permission has a default minimum user role required, the administrator roles can also change that minimum role required for any permission. Non-admin users may access the Permissions grid but cannot make changes to required role settings.
Pre-Defined Security Roles
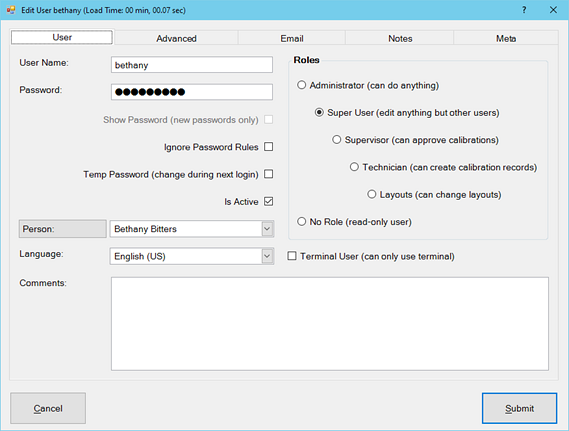
There are six pre-defined security roles, which are Administrator, Super User, Supervisor, Technician, Layouts, and No Role (Read-Only User).
In addition to having a Role, a user may be assigned only as a Terminal User, which means they are not able to access the full application version and can only use the limited CC Terminal Mode.
Hierarchy of Security Roles
Below is an overview summary of predefined user roles and default permissions:
- Read-only users with No Role assigned can view, print, and export grid information within the database.
All five User Roles share the same privileges of Read-only users, in addition to the following:
- Administrator: Highest role can change the work environment, security, and edit Users. Admins have ability to Change Product Key; Modify Security Options; Disable Sign-In Mode; Modify Feature Visibility; Modify minimum Roles required for specific Permissions.
Super User: Second highest role has all permissions of any Role other than the Admin. Can modify most Options and rules. [Cannot change the Security or Feature Visibility Options. Cannot create or edit other Users.] Can edit the Auto Notifications, Codes, Dashboards, Confirm Standards settings, Show Fields settings, and Backup MS Access Database. Can use File menu shortcuts to Open Files / Settings / Data Folders.
Supervisor: Third highest role shares all permissions of lower roles. Can approve calibrations and work orders, remove links between records, edit and delete records. Has permission to edit some settings in program Options.
Technician: Can create and edit records of equipment, calibrations & measurement groups and link standards used, but cannot edit the Cal Technician Name (added automatically) or the final status of the Calibration. Can use Asset Transfer, Record Jobs in Check Out, and use Status Change. Can create and edit and link most data records. Has permission to delete Attachments, Calibration Templates, or Equipment Type records.
Layout: Can make application layout changes relating to the look and feel of the database appearance in the software.
Last Updated: 15 December 2023